
When it comes to plants, it’s not easy to determine where food ends and medicine begins. Take celery as an example, it is clearly a food, but it’s one of those foods that has medicinal or healing properties. In terms of medicinal properties, I classify celery stalks as a salty remedy because of the mineral salts it contains.
Salty herbs aren’t salty in the way we think of foods that contain table salt, sodium chloride. Their mild salty flavor is due to their content of other mineral salts. One function of these salts is to act as electrolytes. Electrolytes are minerals that help water conduct electrical current.
Understanding Electrolytes
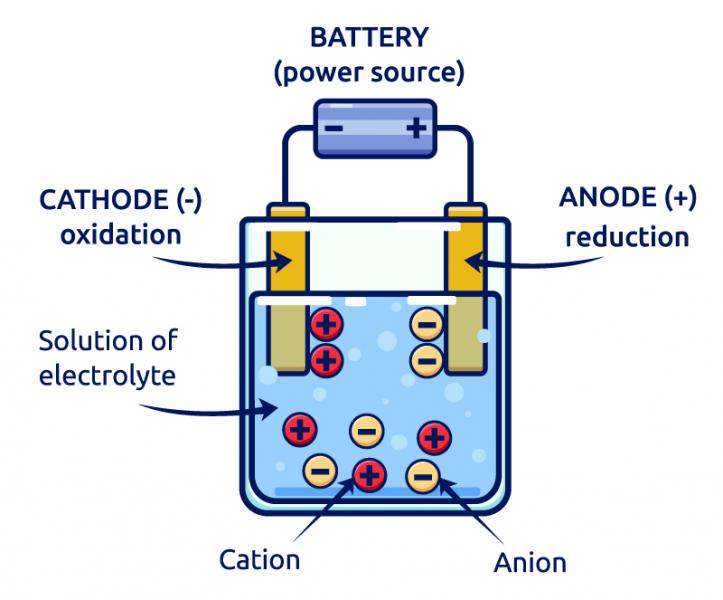 By itself, water itself is not a good conductor of electricity. In fact, if you put electrodes into a beaker of pure water electricity will not flow through it. However, if you add a small amount of table salt to the water, an electrical current will begin to flow. This is what an electrolyte does. It reduces the resistivity of water to electrical flow. This not only helps electrical flow in the tissues, but it also helps keep fluids moving properly through the body.
By itself, water itself is not a good conductor of electricity. In fact, if you put electrodes into a beaker of pure water electricity will not flow through it. However, if you add a small amount of table salt to the water, an electrical current will begin to flow. This is what an electrolyte does. It reduces the resistivity of water to electrical flow. This not only helps electrical flow in the tissues, but it also helps keep fluids moving properly through the body.
There are seven major minerals that act as electrolytes. The four major alkaline electrolytes are calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium. These minerals are electron donors and in an electrolyte solution they are called anions.
The three major acidic electrolytes are chlorine, phosphorus, and sulfur. These minerals are electron borrowers and in an electrolyte solution they are identified as cations.
Mineral Salts
 The alkaline minerals bond to the acidic electrolytes to form salts. Sodium chloride (table salt) is the best known of these, but you can also get sodium sulfate and sodium phosphate. Likewise, you can have potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium phosphate. Calcium and magnesium will also form salts, meaning there are a total of twelve different mineral salts created by these electrolytes. There are other mineral salts found in plants as well. For example, potassium can combine with iodine to form potassium iodide, a mineral salt found in many sea vegetables like kelp and dulse.
The alkaline minerals bond to the acidic electrolytes to form salts. Sodium chloride (table salt) is the best known of these, but you can also get sodium sulfate and sodium phosphate. Likewise, you can have potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium phosphate. Calcium and magnesium will also form salts, meaning there are a total of twelve different mineral salts created by these electrolytes. There are other mineral salts found in plants as well. For example, potassium can combine with iodine to form potassium iodide, a mineral salt found in many sea vegetables like kelp and dulse.
Mineral salts are important to health because they regulate the flow of fluids and energy and these supply minerals for body structures such as bones, muscles, teeth, fingernails, and so forth. Plants that have an abundance of these salts will have a mildly salty flavor, which can be difficult to detect for those of us who have had the salty taste buds dulled by overconsumption of sodium chloride. But with a little practice, you can learn to detect this subtle salty flavor which is present in herbs like parsley, nettle leaf, alfalfa, oat straw, chickweed, wheat grass, barley grass, various seaweeds, and of course, celery. So, with that background, let’s discuss the medicinal uses of celery.
Celery is an Alkalizing Diuretic
 Celery stalks are an alkalizing diuretic. The sodium and potassium salts in them help regulate urinary and lymphatic function, easing water retention and lymphatic congestion. It contains three major mineral salts, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and magnesium chloride.
Celery stalks are an alkalizing diuretic. The sodium and potassium salts in them help regulate urinary and lymphatic function, easing water retention and lymphatic congestion. It contains three major mineral salts, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and magnesium chloride.
It also contains an essential oil containing apiol, which is also found in parsley and has a mildly stimulating effect on the kidneys, increasing urinary output. The magnesium and potassium salts also help rid the body of calcifications, bringing minerals like calcium back into proper solution.
Because of these properties, celery has long been considered a beneficial remedy for gout, rheumatism, and arthritic joints. The fibrous nature of the celery stalk signifies the presence of silicon, an important mineral for healthy hair, skin, nails, and joints. It is also important in the nervous system. For more information on the role of silica, read my previous article Horsetail and Health.
Celery Seed
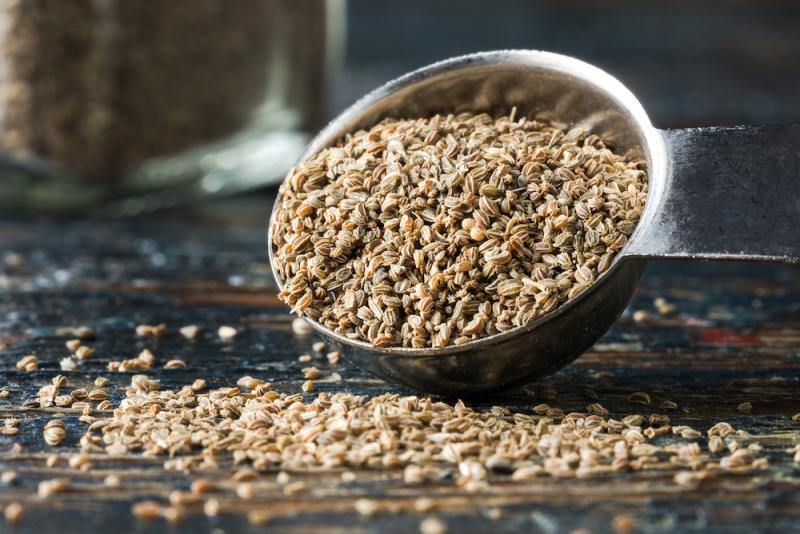 Celery seeds are used both in cooking and as a medicine. They are a stronger diuretic than the stalks and have a more warming aromatic quality. They are also the part of the plant that can be tinctured for use as a medicine. They are contraindicated in pregnancy because they stimulate menstruation and may act as an abortifacient. They are also contraindicated with kidney inflammation, being more suitable for sluggish kidney function.
Celery seeds are used both in cooking and as a medicine. They are a stronger diuretic than the stalks and have a more warming aromatic quality. They are also the part of the plant that can be tinctured for use as a medicine. They are contraindicated in pregnancy because they stimulate menstruation and may act as an abortifacient. They are also contraindicated with kidney inflammation, being more suitable for sluggish kidney function.
The oil in celery seeds can help to lower blood fat levels and has a calming effect on the nervous system. Celery seeds also contain furanocoumarins which can also help lower high blood pressure.
Celery as a Constitutional Remedy
 The Australian naturopath Dorothy Hall suggests that people with a febrile constitution in iridology are celery types. The febrile constitution is a blue-eyed person with many white fibers that give the eye a bluish-white cast. This type tends to have problems with the filtration of acid waste from their body via the kidneys which can lead to problems with over-acidity like the aforementioned gout and rheumatism. However, there are also personality tendencies that go with the febrile constitution.
The Australian naturopath Dorothy Hall suggests that people with a febrile constitution in iridology are celery types. The febrile constitution is a blue-eyed person with many white fibers that give the eye a bluish-white cast. This type tends to have problems with the filtration of acid waste from their body via the kidneys which can lead to problems with over-acidity like the aforementioned gout and rheumatism. However, there are also personality tendencies that go with the febrile constitution.
They tend to have a kind of hyperactive nature, people who are also keeping themselves busy. They have a hard time relaxing and hate to be idle, so they find ways to stay occupied to avoid boredom and a sense of emptiness in their lives. This can also give them a tendency to be “hot and bothered,” that is impatient and irritable. Being constantly busy can lead to anxiety and eventually to feeling burned out.
According to Dorothy Hall the celery person craves water, both for drinking and also for relaxing. They find a warm shower or bath helpful for relaxing their nerves and easing their tendency to muscle and joint pains. However, cold water can actually make them feel worse.
Using Celery for Health
If the above profile applies to you celery may be a good constitutional remedy. You can eat it, juice it, or use a tincture of the seeds. I find a combination of carrot and celery juice a good alkalizing food for helping remove acid waste from the body. You can also just eat it, which means you'd also get the benefits of the fiber and silica in it. I’ve also used celery seeds in making a chicken or turkey salad spread. There’s also a variety of celery that produces a root vegetable called celeriac.
Some people have mild allergic reactions to celery, so if it makes you feel wheezy or tired, it's not the right remedy for you. It’s also not a good idea to use celery seed as a medicine if you’re pregnant or trying to get pregnant, but it’s fine to use if you’re not having periods (amenorrhea) or are having a long cycle with scanty menstruation.
Downloads
Steven's Articles
-

-
The Uplifting Fragrance of Jasmine
Jasmine lifts depression, aids self-confidence,…
February
-

-
Reishi (Ganoderma) Mushroom
A TCM remedy for calming the shen (spirit), balancing…
-

-
Eucommia Bark
A superior tonic that promotes kidney, structural,…
January
-

-
Goldenthread, Phellodendron, and Yellow Root
Three herbal remedies containing the infection-fighting…
-

-
Teasel
A traditional herb for healing bones and joints…
-

-
Barberry and Healthy Personal Boundaries
A thorny shrub for fighting infections and supporting…
December
-
-
The Evidence for Berberine
A yellow alkaloid found in traditional infection-fighting…
-

-
The Sensible Use of Caffeinated Herbs
Kola nuts, guarana, and yerba mate and other herbs…
-

-
The Health Benefits and Problems with Coffee
This popular caffeinated beverage can be beneficial…
October
-

-
Understanding Caffeine & Cellular Adaptation
Preserving the power of caffeine's buzz and the…
September
-

-
Horseradish
A pungent spice for aiding protein metabolism…
-

-
Banaba or Crepe Myrtle
A beautiful tree from Southeast Asia whose leaves…
August
-

-
Monkeyflowers
Flower essences to help see ourselves more clearly…
-

-
Mariposa Lilies
Strengthening the bond between mother and child…
-

-
The Noble Bay Leaf
A common kitchen herb for aiding digestion and…

